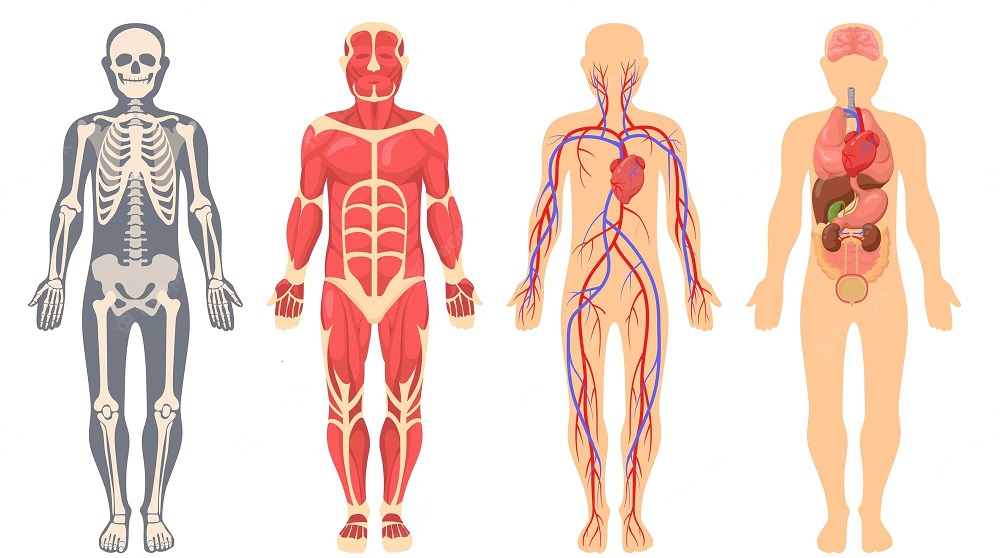
The portal vein is responsible for draining blood from various organs to the liver, it is responsible for hepatic venous circulation. After conducting blood to the liver, nutrients are processed there and toxic substances are expelled from the body.
First of all, it is necessary to define what the portal vein is, which is understood as a thick blood vessel that is responsible for carrying blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver, with the intention that the nutrients required by the body are obtained correctly.
It is structured by the superior mesenteric vein and the spleno-mesenteric trunk. In the case of adults, the portal vein is about 8 centimeters long and is located in the right upper quadrant.
After the toxins are processed by the liver and the required nutrients have been consumed, the blood leaves the organ and goes to the inferior vena cava. Which is in charge of carrying it to the right atrium (heart chamber).
Moments before reaching the liver, the portal vein divides into two parts, each one further subdividing into portal venules. These are the ones that run alongside the hepatic arterioles in the spaces between the hepatic lobes, and these two blood vessels, together with the bile ducts, form the hepatic portal triad. (Via Ken Hub)