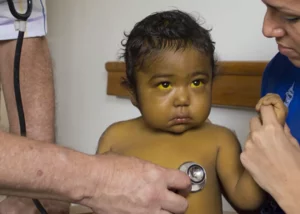
Hemochromatosis is a hereditary disease that results in excess iron in the body, which in turn can lead to organ damage, especially in the liver, pancreas and heart, where it accumulates most. This could cause diseases such as cirrhosis, cancer and irregular heart rate.
Causes
It is due to a genetic mutation that occurs in a gene that controls iron (an essential mineral) that is absorbed from food.
The alteration of the HFE gene is the main cause, it is inherited from both parents.
If you inherit two genes, you can get the disease and pass it on to your children. It is important to mention that inheriting these genes does not mean that the problems caused by the excess of the mineral will occur.
When a gene is inherited, the probability of developing the pathology is reduced. Although it can still transmit the alteration to children, who would have hemochromatosis if they inherited another abnormal gene (from their other parent).
Symptoms
Symptoms usually show their signs in adulthood, specifically in middle age. Generally they present themselves gradually, even the person could notice them when he or she already has too much iron accumulated. Some do not present signs of the disease.

The most common symptoms are:
- Fatigue.
- Diabetes.
- Heart failure.
- Articular pain.
- Loss of sexual desire.
- Cirrhosis.
- Impotence.
- Loss of memory.
- Abdominal pain.
- Skin turns bronze or gray.
Statistically, hemochromatosis occurs more often in men. In the specific case of women, they are more likely to feel the symptoms after menopause.
Diagnosis
Since it is a hereditary disease, when one of the parents is known to have this disease, it is advisable to go to the doctor. You should also see a specialist if you have symptoms and if you suspect you have the disease.
To determine the presence of hemochromatosis, blood tests, genetic testing and biopsy (in some cases) are performed. The patient’s family history will also be reviewed.
The results of the blood test may indicate whether genetic testing is necessary. The biopsy is used to determine if there is liver damage.
Treatment
As the disease consists of an excess of iron, it is sought to decrease it. For this reason, blood is regularly drawn, which contributes to the prevention of further damage, although it does not solve the damage already caused.
The amount of blood to be drawn and the frequency of the procedure will depend on the patient’s conditions (age, state of health, and progression of the disease). If the person also has cirrhosis, an ultrasound should be performed every month in order to rule out liver cancer.
If the person cannot have blood drawn, the treating physician may prescribe a medication for excess iron, which is either injected or swallowed (pill). This medicine collects the excess and the body passes it out in the urine or feces, which is called “chelation.
Additionally, among the recommendations that are usually indicated is to avoid:
- Iron Supplements.
- Alcoholic beverages (increase the risk of liver damage).
- Raw fish and seafood (to prevent infection).
- Vitamin C supplements (increases iron absorption).
- Vitamin complexes containing iron.
In summary, hemochromatosis is an inherited disease that involves too much iron (an essential mineral) accumulating in the body. This excess can result in serious damage to the body, which is why it is important to see a doctor if you suspect that you have the pathology, carry out the relevant examinations and, if necessary, begin the treatment indicated by the specialist.