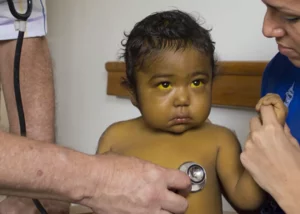
Gaucher disease occurs when the individual lacks the necessary amount of glucocerebrosidase (an enzyme), which results in the accumulation of fatty substances in some organs, especially in the spleen and liver, also in the lungs, bone tissue (increasing the risk of fractures).
As a consequence, the organs become enlarged, which may impair their optimal functioning. If the bone marrow is affected, the clotting process may be compromised.
Classification
There are three types of Gaucher disease:
- Gaucher disease type 1: causes the liver and spleen to enlarge; also causes fractures; even lung and kidney impairment. Does not cause brain damage. It happens to be the most common type of this disease and can occur at any age.
- Gaucher disease type 2 affects the brain, causing significant damage. It occurs in newborn babies, according to statistics, unfortunately most of them die before reaching two years of age.
- Gaucher disease type 3: people with this type may have enlargement of the spleen and liver. It causes brain damage that occurs gradually. It usually arises in childhood or adolescence.
Symptoms
Between each type of the disease, different symptoms are manifested; even the symptomatologies could vary within the same type. For example, siblings with Gaucher disease may have different levels of severity. Some patients have mild symptoms and some have no symptoms at all.
It is a hereditary disease. In most cases, the symptomatology is as follows (manifested in varying degrees):
- Distention and abdominal pain: due to the large enlargement of the liver and spleen.
- Bone problems: weakening of the bones and increased possibilities of fractures. Additionally the person could lose parts of the bone due to this disease, product of the interference in the blood supply to the bones.

- Blood disorders: it has a negative impact on coagulation (by affecting the cells that carry out the process), causing hematomas and nosebleeds. Tiredness may also develop due to anemia (decrease in red blood cells).
- Brain damage: it is rare when Gaucher disease damages the brain. The person may have irregular eye movements, stiff muscles, seizures, and trouble swallowing.
Treatment
Have you ever wondered what the characteristics of Gaucher disease are? All types have one thing in common: Gaucher disease has no cure. However, the existing treatments aim to control the symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
For types 1 and 3 there are treatment options that revolve around drugs as well as therapy. Unfortunately, so far no effective treatment has been developed for the brain damage caused by types 2 and 3.
Broadly speaking, there are several treatments for Gaucher disease. They consist of:
- Enzyme replacement therapy: to replace deficient enzymes with artificial ones. They are administered intravenously in an outpatient procedure every two weeks.
- Medicines that interfere with the development of fatty substances, which accumulate as a result of Gaucher disease.
- Osteoporosis drugs: to treat the weakening of bones caused by Gaucher disease.
- Bone marrow transplantation: for severe cases and if the previous treatments cannot be administered, as it results in a high risk.
- Spleen removal: currently used as a last option, being preferable to try the other treatments.
We suggest consulting the treating physician for more information regarding the treatment indicated to the patient, for example, the side effects. Regarding the nutritional aspect, we also recommend asking the specialist what would be the best diet to follow.