When the liver fails, liver transplantation becomes an alternative, a life expectancy. It is an operation performed in the face of terminal liver disease, although it can be performed in abnormal cases of sudden failure of a healthy liver.
The liver is the large organ that is responsible, among other functions, for eliminating toxins, processing nutrients, medicines and hormones. It also helps direct meals, secretes bile and produces proteins that contribute to blood clotting.
During surgery, the damaged liver is removed and replaced with a healthy one. This organ may come from a deceased donor or a portion of a living donor liver may be placed.

In this sense, it is appropriate to know what are the main causes that produce cirrhosis:
- Fatty liver disease (both those that are caused by alcohol and those that are not).
- Hepatitis B and C.
- Having sclerosing cholangitis or biliary atresia.
- Genetic diseases, including hemochromatosis.
- Certain medications such as methotrexate.
It is also necessary to know that after a liver transplant, the patient’s life changes as he or she becomes a post-transplant patient. Therefore, medical care and recommendations should be maintained.
As explained, during the operation, the damaged liver is removed and a liver (graft) is placed. After connecting the graft to the patient’s body, his immune system will not recognize it as foreign, so it will respond by attacking the organ.
In view of this, it is important to take immunosuppressants for life in order to avoid rejection. It is worth mentioning that the dose is gradually decreasing.
In addition, medicines such as antibiotics and antimicrobials will be necessary (for a while) to prevent infections. Even the ingestion of vitamins and medicines for the tension (for secondary effect of the immunosuppressors, a deficit of vitamins, anemia and hypertension could arise).
Food also plays a fundamental role in avoiding infections. The preparation of meals must have the rules of hygiene and proper cooking, with the aim of eliminating any virus or bacteria that may be present in food, being appropriate to dispense with raw presentations.
Daily the patient has to wash his body, hands, hair and brush his teeth. Hygiene is of significant importance, both for the patient and his or her caregivers, in order to avoid infections.
When the person is discharged, he or she should be aware of the following warning signs, so that he or she can communicate with the treating physicians in case of presenting them
- Fever.
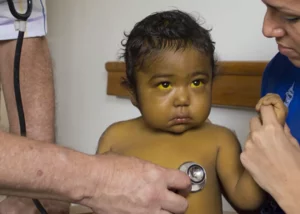
- Jaundice (yellowish color of the skin and mucous membranes). Changes in the color of the feces or urine.
- Headache or tremor.
At the same time, there are a number of risks related to liver transplantation. Among them are complications of the bile ducts, bleeding, mental confusion, including blood clots and seizures.
In this sense, it is essential that patients with end-stage liver disease who qualify for a liver transplant know about the aspects related to the procedure and follow the indications of the treating medical team.
Before performing the transplant, doctors should determine if the patient qualifies for the procedure. This is usually done through various medical tests
On the other hand, it is very helpful for the patient to have the support of family and friends, as well as psychological support in the process of before, during and after the transplant.