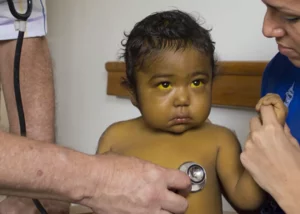
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis refers to the retention of fat in the liver, accompanied by liver cell damage and inflammation, which occurs in those who consume little or no alcohol.
This can result in the formation of scars in the liver, which is known as fibrosis. Cirrhosis (scarring in the liver that affects organ function by deforming its structure) can follow. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis may also cause liver cancer.
Those with very high blood cholesterol, high blood pressure and glucose intolerance are at greater risk of developing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. So do individuals with metabolic syndrome, obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Statistically, between 3 and 12% of American adults suffer from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. It is a disease that is usually asymptomatic; if symptoms occur, they are usually general malaise, tiredness and abdominal discomfort in the upper right part.
It is worth mentioning that nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is a type of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
THE ROLE OF DIET IN HEPATITIS
A healthy and balanced diet can help prevent non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Even doctors often advise people with this disease to eat a healthy diet, especially if they are overweight.

Take note of the recommendations usually given by specialists:
- Limit portion sizes for meals and snacks.
- Eat the right amount of fat.
- Prefer fats from foods such as olive oil, nuts and salmon.
- Avoid fried foods, margarines, lard, vegetable oils and commercial products such as candy, cookies.
- Opt for foods with a low glycemic index, as they have less effect on blood glucose. For example: whole grains, vegetables and fruits.
- Avoid foods and drinks with high amounts of simple sugar, such as soft drinks, juices and sports drinks.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
In addition to eating properly, it is important to be physically active, avoid being sedentary, stay active and play sports.
DIAGNOSIS
To detect the disease it is important to go to the doctor, who will ask questions to find out the person’s medical history. During the physical exam, weight and height are measured, and it is determined if an increase in the liver has occurred. He or she will also look for signs of insulin resistance and cirrhosis.
The patient may then be asked to undergo blood tests, diagnostic imaging (ultrasound, CT and MRI), even a biopsy (removal of a sample of liver tissue) to make sure the diagnosis is made.
TREATMENT
The treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis consists of determining the possible causes that originated it and taking measures to reduce them. Currently, there are no medications to treat this disease directly.
As we mentioned, having a healthy lifestyle, with a healthy and varied diet and exercise, can reduce the risk of suffering from the disease or help treat the cause that caused it.

Treatment may include stopping the intake of certain drugs and measures to treat hyperglycemia. If you are obese, you should gradually reduce your weight. In this sense, it is advisable to consult a nutritionist who will design a nutritional plan adapted to the patient’s requirements.
It has been determined in some studies that the use of certain medications (prescribed for type 2 diabetes) can improve non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in non-diabetic patients.
In case of developing cirrhosis, there are medications for it and other procedures such as surgery. It is worth mentioning that cirrhosis may result in liver failure, which is why a liver transplant may be necessary.
It is also important for the patient to have the support of friends and family; he/she could even attend a psychological support to be able to face the disease.