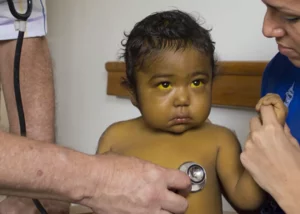
According to Mayoclinlic, this is a “severe liver infection, caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV)”. It is further understood that this disease could become chronic, meaning that it remains in the body for more than 6 months.
Now, is there a cure for hepatitis B? The answer is yes, as long as this infection is acute. However, when hepatitis B becomes chronic there is no specific cure, although there are treatments to cope with it and it is possible to avoid the reinforcement of the virus to reduce liver damage, although in many cases a liver transplant is recommended.
With this in mind, the question of how is hepatitis B spread is more than accurate. It is a virus that spreads from person to person, but it does so in very specific ways such as through different body fluids. However, it is important to note that it is not spread by sneezing or coughing.
Most frequent ways of contagion
The first is through unprotected sexual intercourse. The hepatitis B virus is spread through fluids such as semen, saliva, blood or vaginal secretions. You will contract the disease if any of these enter your body.
Then there is needle sharing, hepatitis B is spread quickly and effectively through “syringes contaminated with infected blood,” explains mayoclinic. In addition to this, there is a form of contagion that prevails for health personnel, although, of course, it could happen to anyone; it is a matter of With this form of contagion, the fear of health personnel with these injections can be combined with an accidental prick, which will be enough to become infected if the needle was contaminated by the virus.
Finally, there is mother-to-child transmission, which occurs when a pregnant woman has HBV and could infect her baby when she gives birth. However, in almost all cases, the child can be vaccinated to prevent infection.
Hepatitis B vaccine
It is common knowledge that vaccines are a key part of health, because thanks to them the immune systems are better prepared to deal with any disease. In this case, hepatitis B is no exception.
It is recommended that adults, adolescents, pre-adolescents and children get vaccinated against HBV, as it helps prevent infection, which in turn avoids future complications.
Hepatitis B can cause liver damage that increases the risk of cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, kidney disease, among others. “Most people who have received the hepatitis B vaccine have lifelong immunity,” reads a Medlineplus article.
It is for this reason, that everyone is advised to take their precautions, in addition to letting them know that the best prevention is vaccination. This will be key if you are in contact with an infected person, as this way you will be protected.