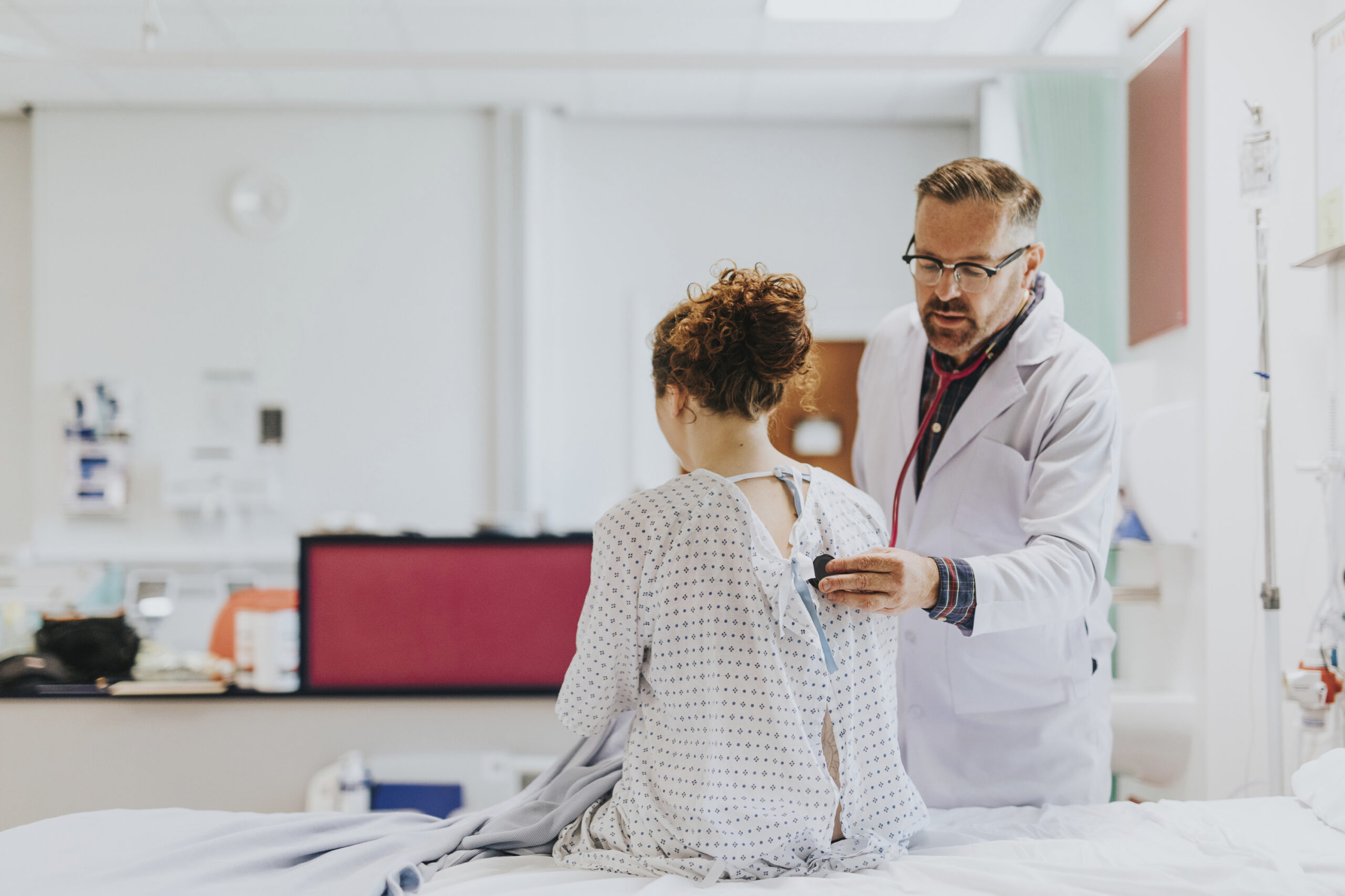
Viral hepatitis depends on viruses such as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, for example. Among these liver conditions there are notorious differences, in the case of B, C and D they can cause acute infections.
The differences between each type of hepatitis are presented below. It should be noted that viral hepatitis can have its origin in types A, B, C, D and E.
Hepatitis A and B
In the case of hepatitis A, it is a virus that causes acute infections, after a few weeks it tends to improve noticeably. It is transmitted through contact with the feces of someone who is already infected. One way to prevent infection is to get the hepatitis A vaccine.
Type B, on the other hand, can develop acute or chronic infections. Before starting any treatment you should consult your doctor, and have him/her assign the test for hepatitis B detection. As with type A, its prevention can be achieved by early vaccination.
It is recommended to see your doctor if you suspect you have the condition.
Hepatitis C
For its detection, the pertinent study is required, and it can cause acute or chronic infections. Early diagnosis will be the key to avoid irreversible liver damage. Some of its symptoms are
- Appearance of hemorrhages with ease
- Fatigue
- Lack of appetite
- Dark colored urine
- Itching of the skin
- Fluid accumulation in the abdominal area
Hepatitis D and E
Transmission of the type D virus is rare since it only occurs in patients who have already contracted type B hepatitis. This is called super infection, since the individual is affected by both viruses.
While E is usually an acute infection, which improves weeks later without any treatment. One form of infection is by drinking water contaminated by feces from a patient who is positive for viral hepatitis type E. As well as by consuming medium-raw meats.
Symptoms of hepatitis:
If any of these signs are present, you should see a specialist as soon as possible. There are symptoms that can occur in any type of hepatitis, among these are:
- Fatigue
- Sudden nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, especially in the upper right side below the lower ribs (in the area of the liver).
- Clay-colored bowel movements
- Loss of appetite
- Low fever
- Dark colored urine
- Joint pain
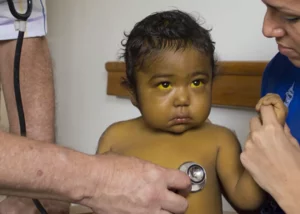
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Intense itching