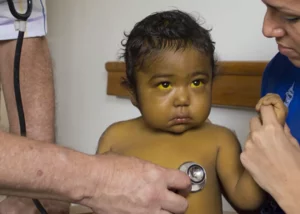
Hepatitis is when the liver becomes inflamed; in the case of neonatal hepatitis, it is when the disease occurs during the first two months of life. In 20% of cases it is due to a virus, which is transmitted during gestation.
The causes of this disease are generally unknown, as well as being commonly due to the presence of viruses in the neonate’s body. However, there is also the possibility that the mother is the one who has the hepatitis virus and transmits it to the baby, either during gestation or after birth.
Of the recognized forms of primary viral hepatitis, only hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a cause of neonatal hepatitis. Neonatal infection with other viruses (e.g., cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus) can cause liver inflammation, along with other manifestations. (Via MSD Manual).
In terms of symptomatology, immediate and noticeable signs may not be present but when present tend to include: jaundice (yellow skin and eyes), weight gain difficulties, liver enlargement, lethargy, abdominal distention and clay-colored stools. In addition, it can cause subclinical disease in early childhood (6 to 12 years).
Depending on the virus and how it evolves, different complications may occur. These include brain damage, liver scarring, easily generated bruising and itching.
What are the treatment options for neonatal hepatitis?
Diagnosis is made by serological tests, which measure HBsAg, HBeAg, antibody to hepatitis B antigen, and quantification of HBV DNA in the blood.
At present there is no pre-established treatment or protocol to follow in a case of neonatal hepatitis, what is done is to provide vitamin supplements, barbiturates and special formulas.
Likewise, correct feeding will be key during recovery. Neither corticosteroids nor anti-hepatitis B immunoglobulin will be useful to fight the infection. All children who have chronic HBV infection should be vaccinated against hepatitis A.
However, in cases where advanced liver scarring (known as cirrhosis) occurs in conjunction with chronic liver disease, transplantation is likely to be considered. It is emphasized that not all cases reach this point, but it may be one of the complications.