Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment in the blood that is produced during the breakdown of old, defective, or damaged red blood cells. When bilirubin levels exceed regular parameters, it could be due to the presence of pathologies in the liver. You already know what bilirubin is; If you want to know more about high bilirubin, keep reading!
On its way through the bloodstream, bilirubin passes through the liver, which is the organ responsible for producing bile (which helps digest food). Finally, both bile and bilirubin are excreted by the human body during the process of evacuating feces.
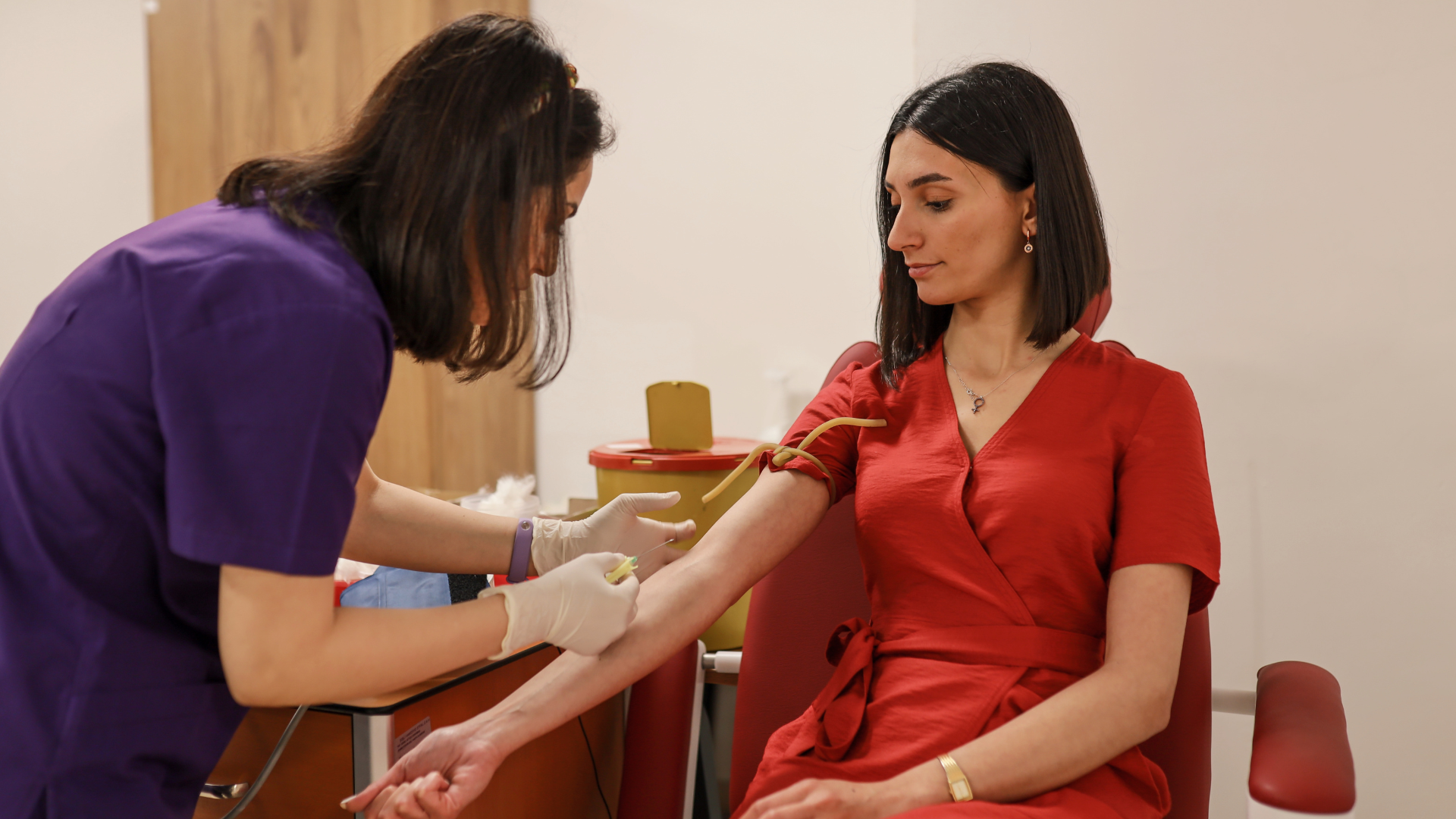
Depending on the patient, it is necessary for the treating physician to indicate a blood test, in order to determine the levels of bilirubin circulating in your body.
To do this, the person must go to a service provider that has a duly authorized laboratory, where they will take a blood sample to be analyzed. To guarantee that the results obtained are reliable, it is required that the patient comply with the medical recommendations prior to the blood test.
Is it necessary to perform the bilirubin test?
Among the causes that can motivate the treating physician to request an examination, to determine the levels of bilirubin in the blood of a patient are the following:
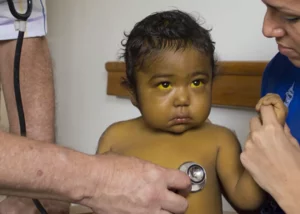
- Determine if the patient suffers from jaundice, (in the presence of a yellowing of their skin and eyes), which could be due to high levels of bilirubin in the blood.
- Detect any type of obstruction of the bile ducts in the liver or, depending on the case, in the gallbladder.
- Discover liver-type pathologies such as hepatitis or monitor their progress to improve the patient’s quality of life.
- For newborns, this test is often done to measure bilirubin levels to check for jaundice.
- Assess whether the patient presents a clinical picture of anemia caused by the destruction of red blood cells.
- Investigate possible drug toxicity.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of a medical treatment in the specific case of the patient.
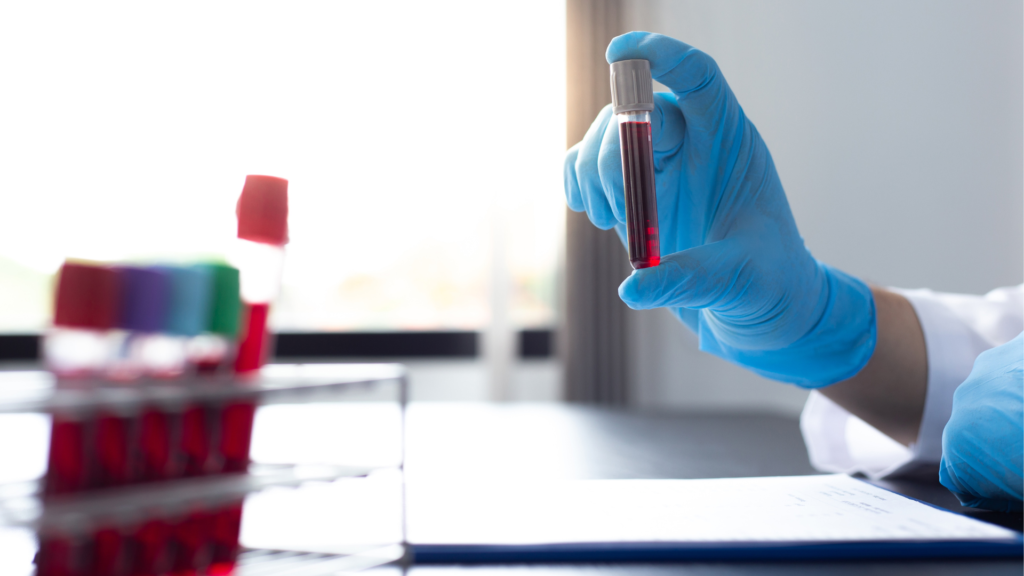

Analysis results
Bilirubin values are expressed through the concentration level contained in the blood. Once the analysis is done, the results can be classified into direct and indirect or total bilirubin.
What is direct bilirubin?: also called conjugated, it has the characteristic that it dissolves in water and is produced in the liver from the indirect bilirubin that has reached this organ contained in the blood that circulates in the organism.
What is indirect bilirubin?: Known as unconjugated, it is characterized by not being soluble in water. It circulates through the body until it reaches the liver where it is transformed into direct or conjugated bilirubin.
What is total bilirubin?: It is the product of the combination of direct and indirect bilirubin
It is appropriate to note that direct and total bilirubin levels are obtained from direct measurements in the blood, while indirect bilirubin levels are deduced from total and direct bilirubin measurements.
Low levels of bilirubin in the blood are generally not a cause for concern for the treating physician and his or her patient. On the other hand, when the bilirubin values are above normal, the alarms go off, as it can indicate problems due to high bilirubin, that is, that something is affecting the body, including different types of liver or bile duct pathologies.
The normal results for an adult person of the levels of bilirubin in the blood can be highlighted as follows:
Direct: 0.0 – 0.3 mg/dL or 1.7 – 5.1 mcmol/L
Indirect: 0.2 – 1.2 mg/dL or 3.4 – 20.5 mcmol/L
Total: 0.0 – 1.4 mg/dL or 1.7 – 20.5 mcmol/L
The analysis of the amount of bilirubin in the blood can give results that differ somewhat from one laboratory to another. Also, they vary slightly when compared between blood test results from an adult male versus a woman or child.
The important thing is to follow medical recommendations and keep an eye on bilirubin levels to detect, rule out, or monitor obstructive-type diseases of the bile ducts in the liver or, depending on the case, in the gallbladder, associated with high bilirubin.