Fatty liver, known in medical terms as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which the liver accumulates excess fat. Although this problem can be triggered by a variety of causes, diet plays a key role in its prevention and management. In this article, we will explore how a balanced diet can be a key ally in the fight against fatty liver, especially the non-alcoholic type, and provide examples of menus designed for patients with this condition.
Balanced Diet: Fatty Liver Diet
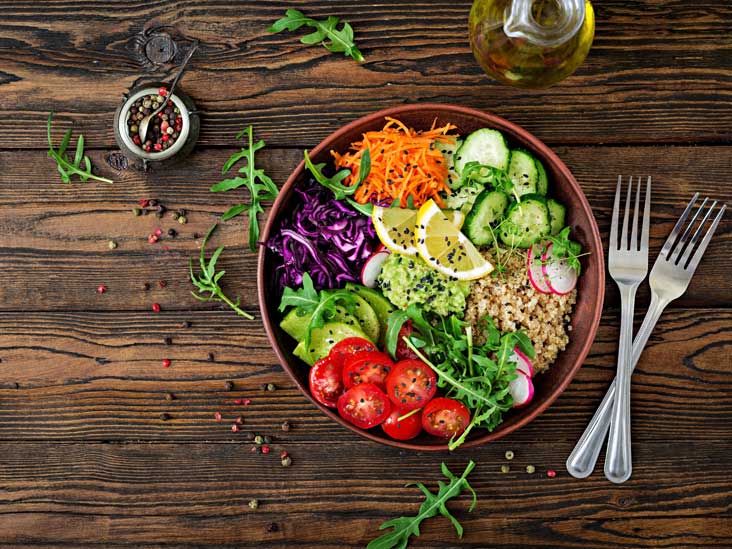
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells in people who do not consume a significant amount of alcohol. A balanced diet can be a vital tool in the management and prevention of this condition. The main focus should be on reducing the intake of saturated fats and refined sugars, while increasing the intake of foods rich in fiber, antioxidants and healthy fatty acids.
Fiber plays an important role in controlling fatty liver. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains not only aid in digestion, but also regulate blood glucose levels and reduce insulin resistance, a factor associated with the development of fatty liver. Antioxidants present in fruits and vegetables protect the liver from oxidative stress, while healthy fatty acids, such as those found in olive oil, nuts and fatty fish, have anti-inflammatory properties and may contribute to liver health.
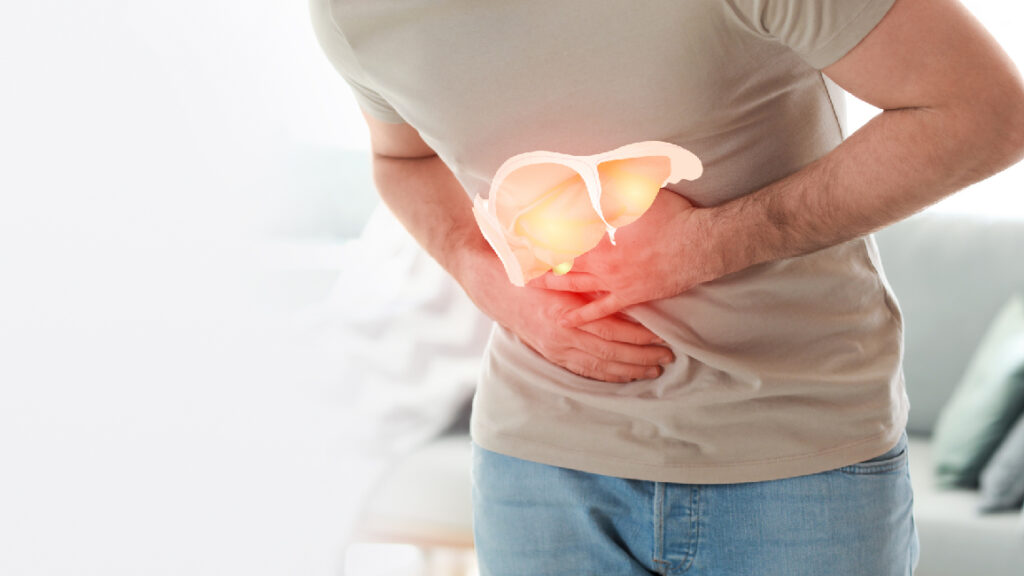
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver: A Diet That Makes a Difference
The key to addressing non-alcoholic fatty liver lies in a diet that minimizes the burden on the liver and promotes its regeneration. It is important to consult a medical specialist for your personalized dietary specifications. Here are some specific tips on how to structure an effective diet:
- Limit Saturated Fats: Reduce consumption of fatty meats, full-fat dairy products and fried foods. Opt for lean meats, such as skinless chicken, turkey and fish.
- Opt for Complex Carbohydrates: Choose whole grains over refined grains. Complex carbohydrates are digested more slowly, avoiding spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Include Lean Protein Sources: Protein is essential, but choose low-fat options, such as legumes, fish and tofu.
- Prioritize Vegetables and Fruits: These foods are full of fiber, vitamins and antioxidants that benefit liver health.
- Consume Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fatty fish such as salmon, walnuts and chia seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Control Portion Size: Avoid excess calories, as overweight and obesity are linked to nonalcoholic fatty liver.
Additional Tips and Final Considerations
In addition to following a balanced eating plan, there are several additional tips that can contribute to effective fatty liver management:
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking enough water is essential for maintaining good liver function. Water helps flush out toxins and maintain adequate hydration.
- Limit Sugar Intake: Excess sugar can contribute to insulin resistance and the development of liver fat. Reduce intake of sugary drinks, sweets and desserts.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity not only helps control weight, but also improves insulin sensitivity and promotes liver health.
- Avoid Alcohol: Although it is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, it is important to remember that alcohol can worsen the liver condition. Abstaining from alcohol is essential.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on liver health. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can be beneficial.
- Medical Supervision: It is crucial to work in collaboration with a healthcare professional, such as a physician or dietitian, to develop a dietary plan tailored to individual needs and follow up appropriately.

In Summary
Diet plays a vital role in the prevention and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Opting for a diet rich in fiber, antioxidants and healthy acids, while avoiding saturated fats and refined sugars, can contribute significantly to liver health. In addition to following a proper eating plan, it is important to adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, adequate hydration and stress management. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making major changes to your diet or lifestyle, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions.
Ultimately, addressing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can make a difference in liver health and overall quality of life. The important thing is to seek the advice of a medical specialist. With commitment and focus, it is possible to effectively improve and prevent this condition.