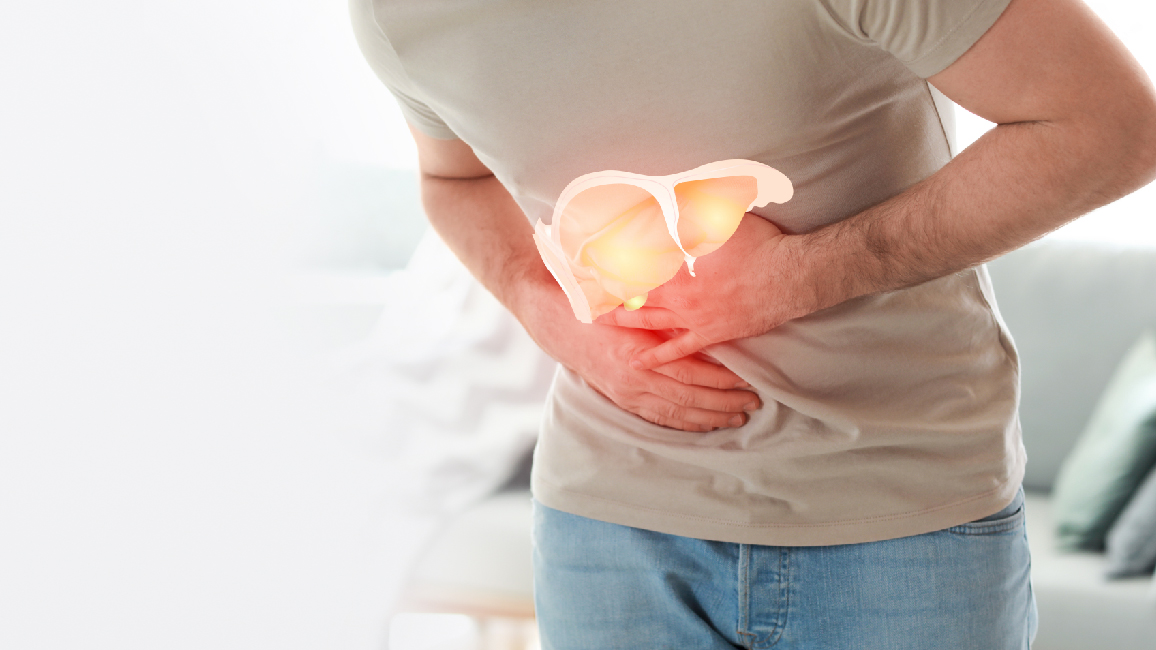
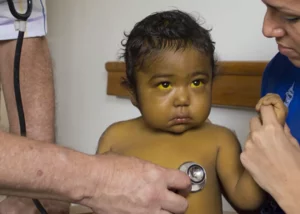
Hepatitis is a viral disease affecting the liver, and understanding its modes of transmission is crucial to prevent its spread. Here are seven common ways hepatitis can be transmitted, the major risks associated, and how to act in case of possible contagion.
How is it Transmitted?
1. Contact with Infected Blood: Direct contact with the blood of an infected person is a primary transmission route, especially through shared needles or unsafe medical procedures.
2. Unprotected Sexual Relations: Hepatitis B and C can be transmitted through unprotected sexual relations, making consistent condom use crucial to prevent transmission.
3. From Mother to Baby: Transmission of hepatitis can occur from mother to child during childbirth. However, vaccination and proper medical care can significantly reduce this risk.
4. Consumption of Contaminated Water or Food: Hepatitis A and E often spread through contaminated water or food. Handwashing and consuming safe foods are key preventive measures.
5. Intravenous Drug Use: Sharing needles among intravenous drug users increases the risk of hepatitis B and C transmission. Prevention focuses on access to sterile equipment.
6. Unsafe Tattoos or Piercings: Procedures performed with non-sterile instruments can be a transmission route. Choosing establishments with safe practices is essential.
7. Sharing Personal Grooming Items: Personal items like toothbrushes or razors can transmit hepatitis if shared with an infected person.
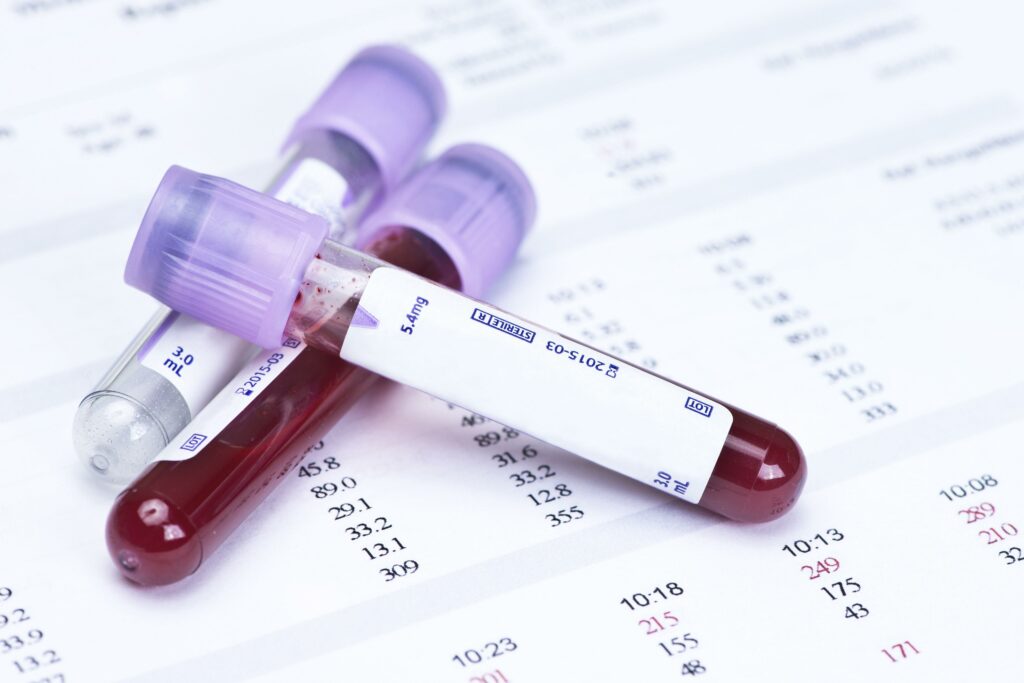
What are the Major Risks?
Major risks are associated with practices involving direct contact with blood, unprotected sexual relations, and unsafe medical or aesthetic procedures. Additionally, poor sanitation conditions increase the risk of transmission through contaminated water or food.
How to Act in Case of Possible Contagion?
In case of possible contagion, seeking immediate medical attention is essential. Early detection and proper treatment can prevent long-term complications. Additionally, informing individuals with whom recent contact has occurred facilitates preventing disease spread.

Summary
Hepatitis can spread through contact with infected blood, unprotected sex, needle-sharing, and more. Major risks include unsafe medical procedures and lack of sanitation. In case of possible contagion, seeking immediate medical attention and adopting safe practices are crucial to prevent the spread of liver disease.