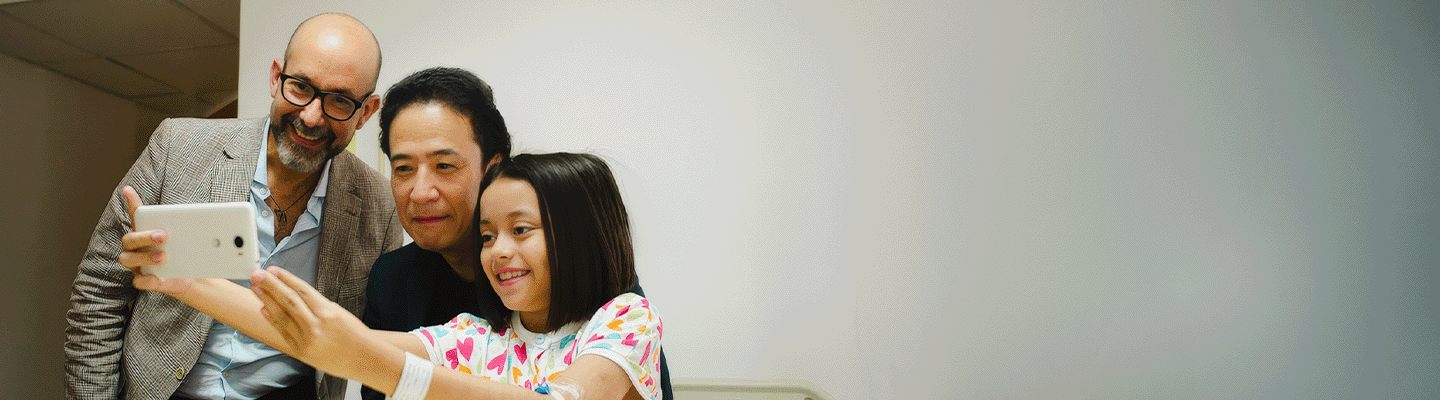¿Quiénes somos?
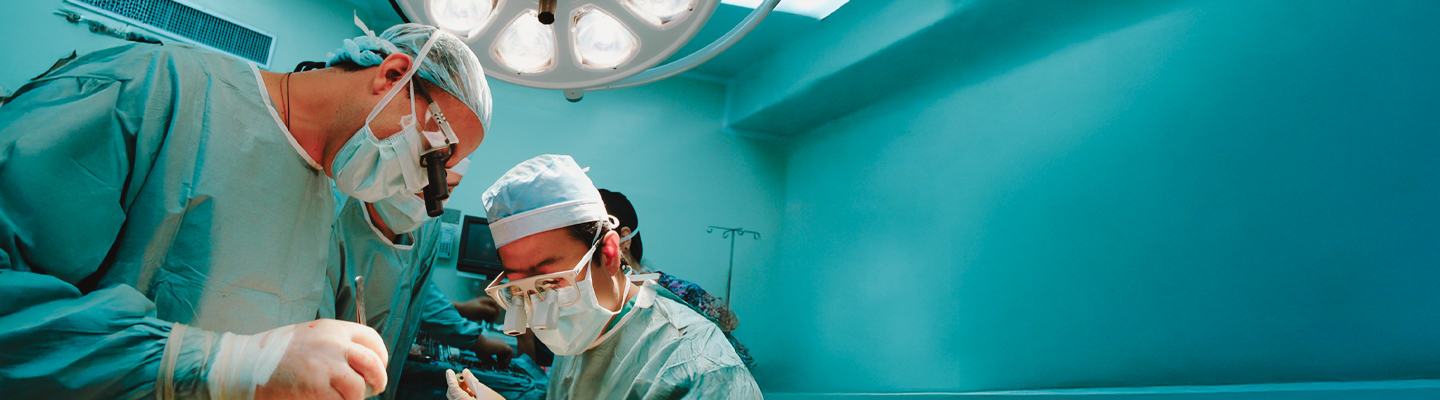
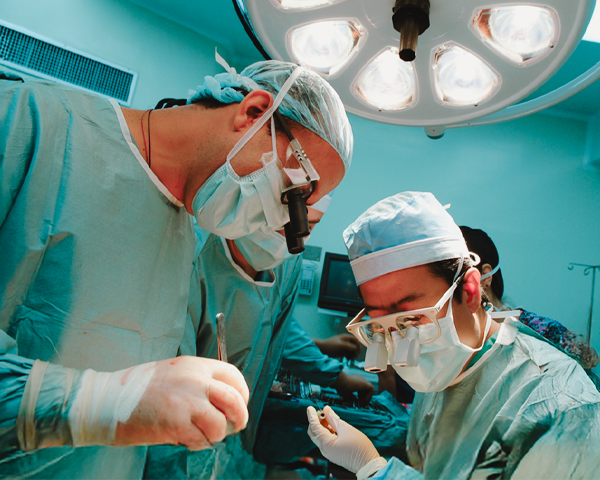
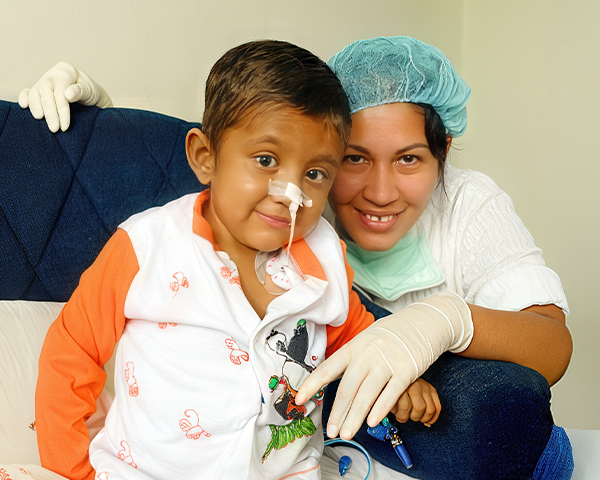
Fundahígado América (FHA) es una organización de caridad sin fines de lucro, registrada en Estados Unidos. Fundada como una organización independiente exenta de impuestos tipo 501 (c) 3. FHA fue creada con la misión principal de capacitar al personal médico de distintos países de Latinoamérica para ofrecer el trasplante hepático pediátrico de vivo a vivo (THPVV) y mejorar la calidad de la atención de los niños que padecen enfermedades hepáticas complejas en países de América Latina y el Caribe.