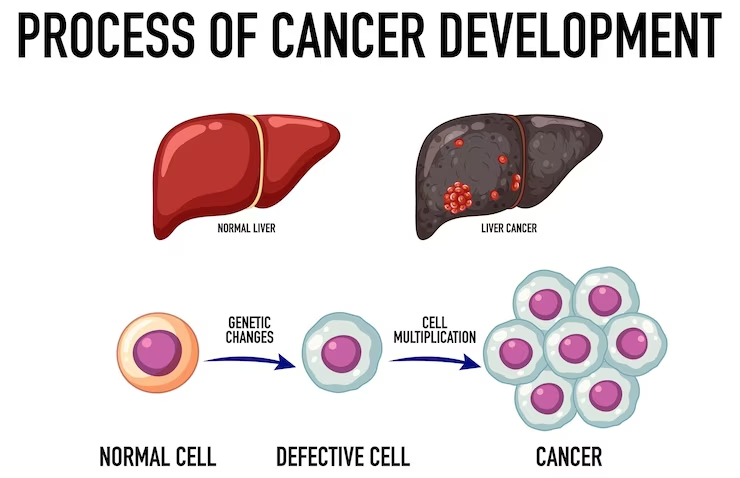
Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide. It is important to recognize the signs of this liver disease and its possible causes.
Liver cancer begins in the liver cells and there are several types. The most common is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.
Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that starts in liver cells. When it starts in another area of the body, such as the colon, lung or breast, and then goes to the liver, it is called metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer.
Symptoms of liver cancer
Most people have no signs and symptoms in the early stages of primary hepatic cancer. When signs and symptoms are present, they may include the following:
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the upper abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- General weakness and fatigue.
- Abdominal swelling.
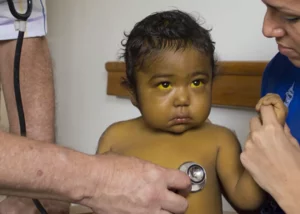
- Yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
- White or whitish stools.
It should be noted that there may be no symptoms until the cancer is already advanced. This makes treatment difficult. Doctors use tests that examine the organ and blood to diagnose hepatic cancer. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or liver transplantation.
Causes and risk factors
As mentioned above, HCC is the most common type of hepatic cancer in adults. It usually occurs in people with chronic (long-term) liver disease caused by infection with a hepatitis virus or cirrhosis. It should be noted that men are more prone to HCC than women.
Although people with several risk factors are more likely to have this liver complication, it does not mean that they will necessarily have the disease. The risk factors are as follows:
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
- Cirrhosis.
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Aflatoxin B1.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
- Cigarette smoking.
It is necessary to be aware of the signals our body gives off, and the lifestyle we lead in order to prevent this disease. Anything that increases the probability of having cancer is called a risk factor. Prevention consists of avoiding risk factors and increasing protective factors.