Liver infection, also known as hepatitis, is a serious condition that can have various causes. Understanding the symptoms and common causes of liver infections is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore what liver infection feels like, the consequences of an infected liver, and the leading cause of liver disease. Let’s dive in!
What Does Liver Infection Feels Like?
Liver infections often present with a range of symptoms that may vary depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Fatigue and Weakness: persistent tiredness and weakness are common symptoms of a liver infection. This can be attributed to the liver’s reduced ability to metabolize nutrients, leading to decreased energy levels.
- Abdominal Pain and Discomfort: many individuals with liver infections experience abdominal pain or discomfort, particularly in the upper right quadrant. This discomfort may range from mild to severe and can be accompanied by bloating or a feeling of fullness.
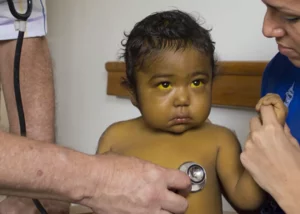
- Jaundice: yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice, is a characteristic symptom of liver infection. It occurs when the liver fails to effectively process bilirubin, resulting in its accumulation in the body.
- Digestive Issues: liver infections can cause digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Changes in appetite and weight loss are also common.
- Dark Urine and Pale Stools: a liver infection may lead to changes in urine and stool color. Urine may become darker, while stools can appear pale or clay-colored due to the improper breakdown of bilirubin.
If you experience any of these symptoms persistently, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
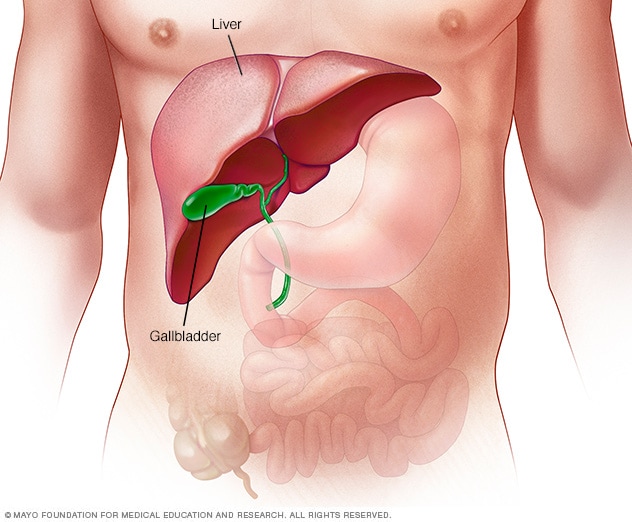
What Happens if the Liver Is Infected?
An infected liver can have severe consequences for your overall health. The liver performs vital functions such as detoxifying the body, producing bile for digestion, storing vitamins and minerals, and regulating blood sugar levels. When the liver is infected, these functions can be compromised, leading to the following complications:
- Cirrhosis: prolonged liver infection can result in the development of scar tissue, leading to a condition called cirrhosis. Cirrhosis can disrupt liver function and may progress to liver failure if left untreated.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: in advanced stages of liver disease, the liver’s inability to remove toxins from the blood can lead to a condition called hepatic encephalopathy. This can cause confusion, personality changes, and even coma.
- Liver Cancer: certain types of liver infections, such as chronic hepatitis B or C, can increase the risk of developing liver cancer. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment are essential to reduce this risk.
The Most Common Cause of Liver Disease
The leading cause of liver disease and infection is viral hepatitis. Hepatitis viruses, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, can infect the liver and cause inflammation. Hepatitis B and C are particularly prevalent and can progress to chronic infections.
Other common causes of liver infection include:
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: long-term alcohol abuse can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis if not addressed.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD occurs when fat builds up in the liver, typically in individuals with obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: in this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the liver, leading to inflammation and potential liver damage.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the common causes of liver infections are essential for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If you experience any persistent symptoms or concerns related to your liver health, it is crucial to seek medical attention. Viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and autoimmune hepatitis are among the primary causes of liver infections.
By prioritizing liver health, adopting a balanced lifestyle, and seeking early medical intervention when needed, you can reduce the risk of liver infections and their potential complications. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis, personalized advice, and proper management of liver health.