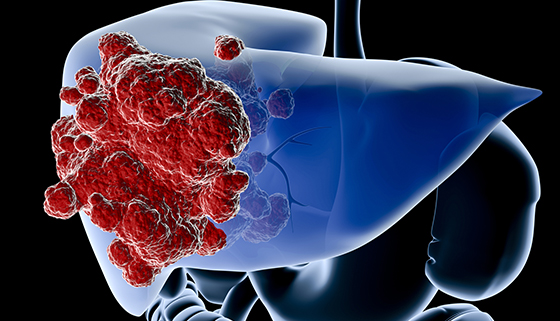
Liver cancer is a serious condition that affects millions of people worldwide. As with any medical condition, there are numerous myths and misconceptions surrounding liver cancer that can lead to confusion and misinformation. In this article, we will debunk some of the common myths associated with liver cancer and provide you with accurate information to increase your awareness and understanding of this disease.
Myth 1: Liver Cancer Has a High Survival Rate
Fact: The survival rate of liver cancer varies significantly depending on the stage at which it is diagnosed. Generally, liver cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, which can lower the overall survival rate.
According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for liver cancer is around 20%, but this number can be much higher if the cancer is detected and treated early. It’s crucial to understand that early detection through regular medical check-ups and screenings can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment and a higher survival rate.
Myth 2: Cancer Treatment Always Involves Surgery
Fact: While surgery can be an effective treatment option for some cases of liver cancer, it’s not the only approach available. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the extent of metastasis, if any.
Treatments for liver cancer can include surgery, liver transplantation, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual patient’s needs and the characteristics of their cancer.
Myth 3: Liver Cancer and Metastasis Are the Same Thing
Fact: Metastasis refers to the spread of cancer from its original location to other parts of the body. Liver cancer can indeed metastasize, meaning it can spread to other organs or tissues. However, metastasis is not the same as liver cancer itself. Liver cancer that has spread to other organs is still considered liver cancer and is treated as such. It’s important to differentiate between the primary cancer site and any secondary sites of metastasis when discussing treatment options and prognosis.
Myth 4: Only People Who Consume Alcohol Get Liver Cancer
Fact: While excessive alcohol consumption is a risk factor for liver cancer, it is not the only cause. Chronic infections with hepatitis B or C viruses are among the most common causes of liver cancer worldwide.
Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, exposure to certain chemicals, and genetic factors. It’s important to note that individuals who do not consume alcohol can still develop liver cancer if they have other risk factors.
Myth 5: Liver Cancer Is Always Symptomatic
Fact: In its early stages, liver cancer may not produce noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and swelling in the abdomen may develop.
However, these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions. Regular medical check-ups and screenings are essential for detecting liver cancer in its early stages, when treatment is most effective.
In conclusion, understanding the facts about liver cancer is crucial for accurate information and informed decision-making. Myths and misconceptions can hinder proper understanding and delay diagnosis and treatment.
By dispelling these myths and spreading accurate knowledge, we can promote early detection, better treatment outcomes, and improved quality of life for individuals affected by liver cancer. Remember, staying informed is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer.
Myth 6: Liver Cancer Is Always Fatal
Fact: While liver cancer can be a serious and life-threatening condition, it is not necessarily always fatal. As mentioned earlier, the survival rate for liver cancer varies depending on factors such as the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the effectiveness of treatment.
Advances in medical research and treatment options have led to improved outcomes for many individuals with liver cancer. Early detection, appropriate treatment, and a comprehensive care plan can significantly increase the chances of survival and long-term management of the disease.
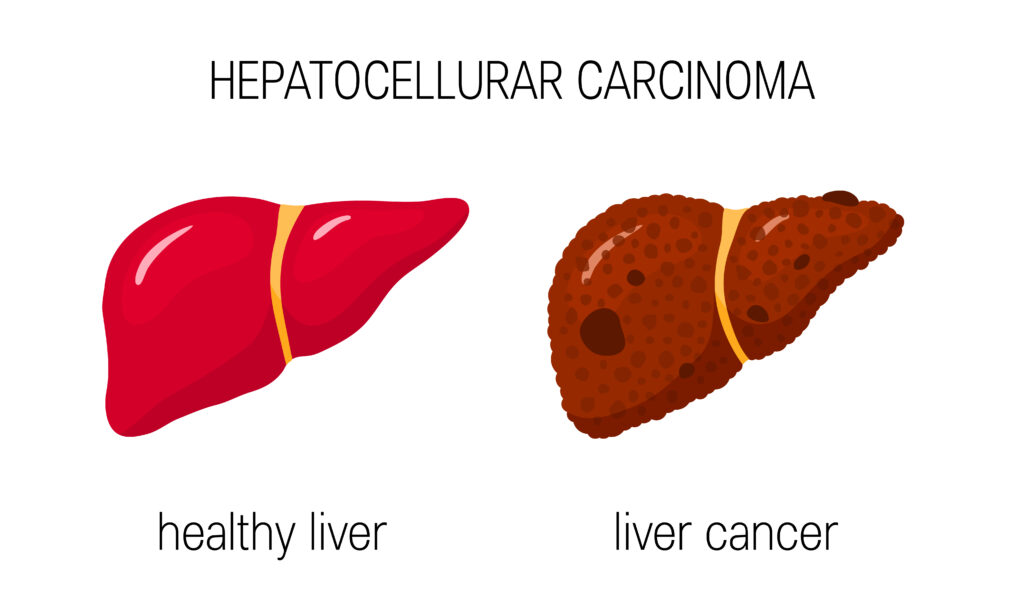
Myth 7: Liver Cancer Only Affects Older Adults
Fact: While liver cancer does have a higher incidence among older adults, it can affect individuals of any age. Risk factors such as viral infections, genetic predisposition, and exposure to certain toxins can contribute to the development of liver cancer in younger individuals as well.
It’s important for people of all ages to be aware of the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with liver cancer.
Myth 8: Liver Cancer Is Not Preventable
Fact: While not all cases of liver cancer are preventable, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, can help lower the risk of developing liver cancer.
Additionally, getting vaccinated against hepatitis B and C viruses and practicing safe sex can also reduce the risk of chronic infections that can lead to liver cancer.
Myth 9: There’s Nothing You Can Do If You’re Diagnosed with Liver Cancer
Fact: A diagnosis of liver cancer is undoubtedly challenging, but there are many treatment options available to help manage the disease and improve quality of life. Working closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and support services, can help individuals navigate their treatment journey.
New advancements in cancer research and personalized medicine continue to expand the range of treatment options, giving hope to patients and their families.
Myth 10: Liver Cancer Is Contagious
Fact: Liver cancer itself is not contagious. It cannot be spread through physical contact, sharing personal items, or being in close proximity to someone with the disease. The risk factors for liver cancer, such as hepatitis B or C infections, are transmitted through specific routes like unprotected sex, sharing needles, or exposure to contaminated blood.
However, liver cancer itself cannot be directly transmitted from one person to another.
Myth 11: Herbal Supplements Can Cure Liver Cancer
There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that herbal supplements alone can cure liver cancer. While some herbs and natural compounds may have potential health benefits, they should never be relied upon as a sole treatment for a serious medical condition like liver cancer. Treatment for liver cancer should be based on evidence-based medical approaches and under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals.
Myth 12: Liver Cancer Always Causes Obvious Symptoms
As mentioned earlier, liver cancer may not always cause noticeable symptoms, especially in its early stages. This is why regular medical check-ups and screenings are crucial, especially for individuals with risk factors such as viral infections or a family history of liver disease. Detecting liver cancer at an early stage can significantly improve treatment outcomes and increase the chances of successful intervention.
Myth 13: Once Treatment is Over, There’s No Need for Follow-up
After completing treatment for liver cancer, regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential. Follow-up visits allow healthcare professionals to monitor the patient’s progress, assess any potential recurrence, manage side effects, and provide ongoing support. Liver cancer can have long-term effects on the body, and ongoing medical supervision can help manage any complications that may arise after treatment.
Myth 14: Only People with Risk Factors Need to Worry About Liver Cancer
While certain risk factors, such as hepatitis infections and excessive alcohol consumption, can increase the likelihood of developing liver cancer, it can still affect individuals without these risk factors. Some cases of liver cancer have no known risk factors, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, getting regular check-ups, and staying aware of potential symptoms. Being proactive about your health can help catch any potential issues early on.
Myth 15: Liver Cancer Is Not a Significant Health Concern
Liver cancer is a serious health concern that should not be underestimated. It is the sixth most common cancer worldwide and has a high mortality rate. Ignoring the risks and dismissing the importance of early detection and proper medical care can have serious consequences. Being informed and taking preventive measures is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being.
In conclusion, understanding the realities of liver cancer and dispelling the myths surrounding it is essential for accurate information and effective prevention and management strategies. By being aware of the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk, seek early diagnosis, and make informed decisions about their health.
Education and awareness are powerful tools in the fight against liver cancer and can contribute to better outcomes and improved quality of life for those affected by this disease.