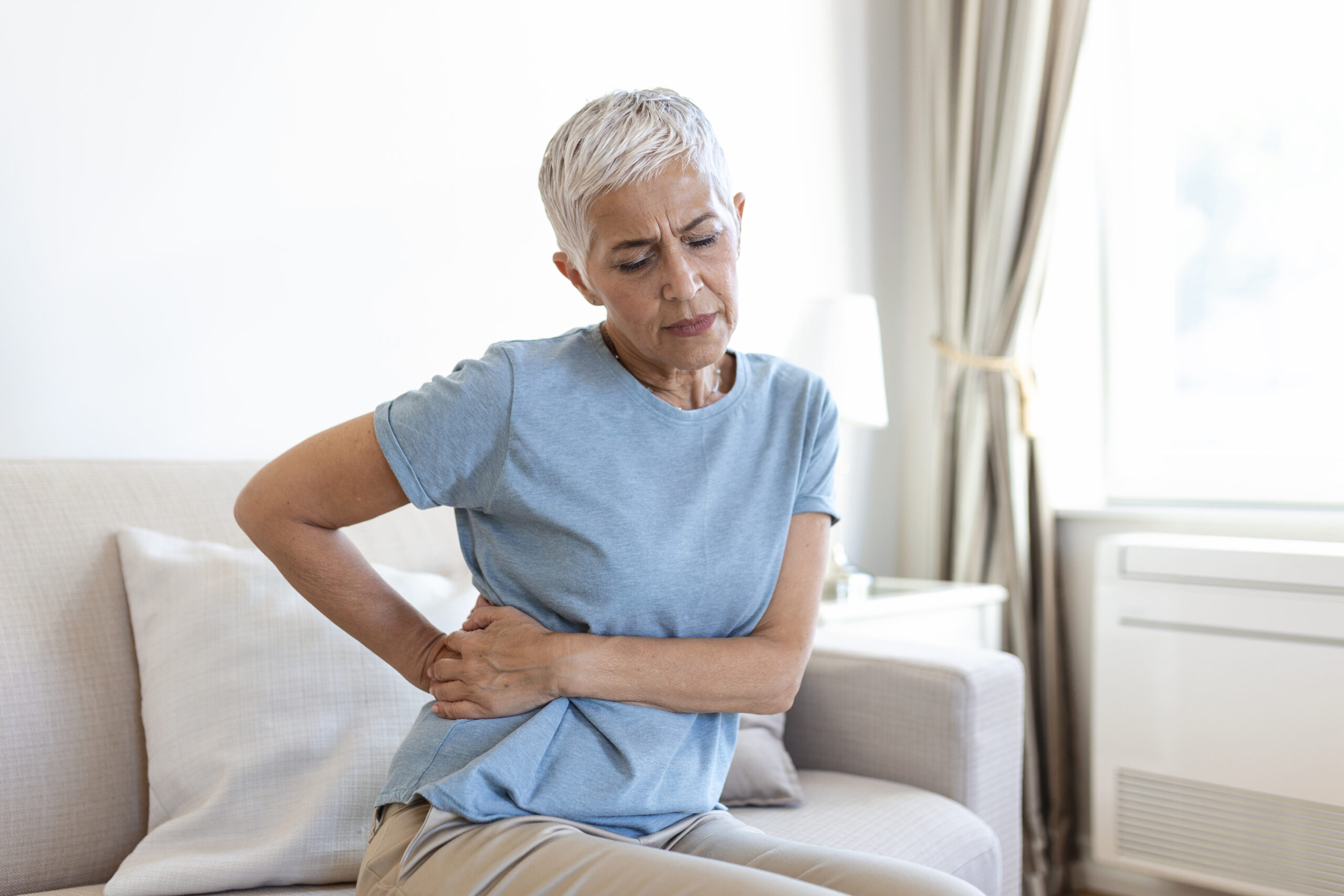
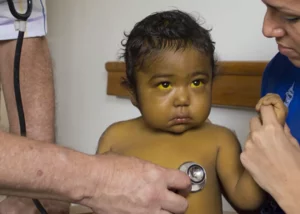
“Hepatomegaly” or inflamed liver is an abnormality consisting of enlargement of the organ in question. This condition could represent liver disease, congestive heart failure, or cancer.
The liver is one of the largest organs of the human body, which is compared to the shape of a soccer ball and is located in the upper right part of the abdomen. However, its dimension may change with respect to age, sex and body proportions.
When the liver is inflamed, there may be no symptoms other than enlargement. However, there may be discomfort such as abdominal pain, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Causes of inflamed liver
his disease can be interpreted as the first sign or response of a more serious condition within our organism, and the causes of the growth in the organ can be liver diseases such as:
- Cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis caused by a virus, including hepatitis A, B and C, or caused by infectious mononucleosis.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- The accumulation of abnormal proteins in the liver (amyloidosis).
- A genetic disorder that causes copper to accumulate in the liver (Wilson’s disease).
- A disorder that causes iron accumulation in the liver (hemachromatosis).
- The accumulation of fatty substances in the liver (Gaucher disease).
- Fluid-filled sacs in the liver (liver cysts).
- Non-cancerous liver tumors, including hemangiomas and adenomas.
- Obstruction of the gallbladder or bile ducts.
- Toxic hepatitis.
It may also be a first sign of cancer that begins elsewhere in the body and spreads to the liver, leukemia, liver cancer or lymphoma. In turn, it may represent heart or blood vessel problems related to a blockage of the veins draining the liver (Budd-Chiari syndrome), heart failure or inflammation of the tissue surrounding the heart (pericarditis).
What causes an “hepatomegaly”?
It is common for the liver to become enlarged if liver disease is present. Factors that can increase the risk of liver problems include the following:
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol in large quantities can be harmful to the liver.
- Excessive doses of medications, vitamins or supplements: taking higher than recommended doses of vitamins, supplements or over-the-counter or prescription medications may increase the risk of liver damage.
According to the Mayoclinic website, an overdose of acetaminophen is the most common cause of acute liver failure in the United States. In addition to being a component in over-the-counter pain relievers such as Tylenol, it is found in more than 600 medications, both over-the-counter and prescription.
- Herbal supplements: some supplements, such as black cohosh, ma huang and valerian, may increase the risk of liver damage.
- Infections: infectious, viral, bacterial or parasitic diseases may increase the risk of liver damage.
- Hepatitis viruses: Hepatitis A, B and C can cause liver complications.
- Poor eating habits: being overweight increases your risk of liver disease, as does eating unhealthy foods that contain large amounts of sugar or fat.
How to prevent liver diseases?
Although liver diseases can be generated by a considerable number of situations, the good news is that they can be prevented if we are not talking about a major complication.
Maintaining a healthy diet, drinking alcohol in moderation, following the indications when taking vitamins and medications, limiting contact with chemical substances such as insecticides, maintaining a healthy and appropriate weight, avoiding smoking and taking supplements under medical indications are the best recommendations to avoid problems with an inflamed liver and to keep this important organ in good condition.